Atrial septal aneurysm, Mitral Valve Prolapse Syndrome, Echocardiography, Real Time-3D-Echocardiography
A 68-year-old male presented to the out-patient clinic with history of intermittent palpitations and fatigability for past seven months. On cardiovascular system examination, mid-systolic click and pan-systolic murmur grade III/VI were audible at the apex with radiation to the base of heart. Echocardiographic study revealed atrial septal aneurysm (Figure 1, Figure 2, Video 1 and Video 2), along with prolapse of Posterior Mitral Leaflet (PML) into left atrium (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Color-doppler echocardiography revealed severe eccentric mitral regurgitation MR) jet impinging on atrial septal aneurysm with vena-contracta width of 10.9 mm (Figure 4 and Video 3).
Atrial Septal Aneurysm (ASA) is a congenital deformity of the inter-atrial septum with a prevalence of 1-2% in the adult population. It is usually associated with Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO), Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), Mitral Valve Prolapse Syndrome (MVPS), TVPS, Marfan's syndrome and aortic dissection.
None.
None.
All authors contributed equally to the scientific content, designing and writing of this manuscript.
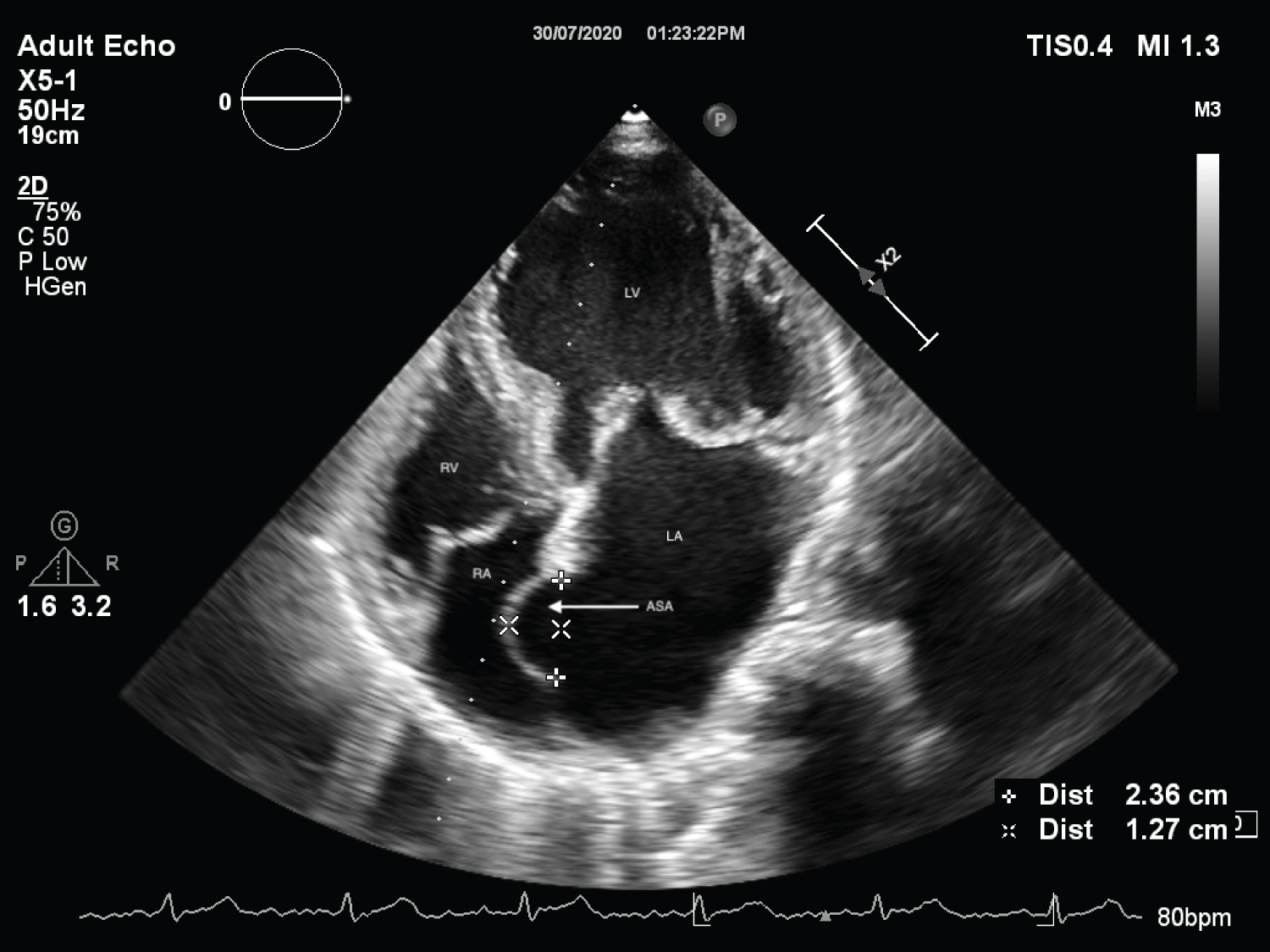
Figure 1: Apical 4 chamber view on 2-Dimensional echocardiography showing prolapse of PML and interatrial septal aneurysm.
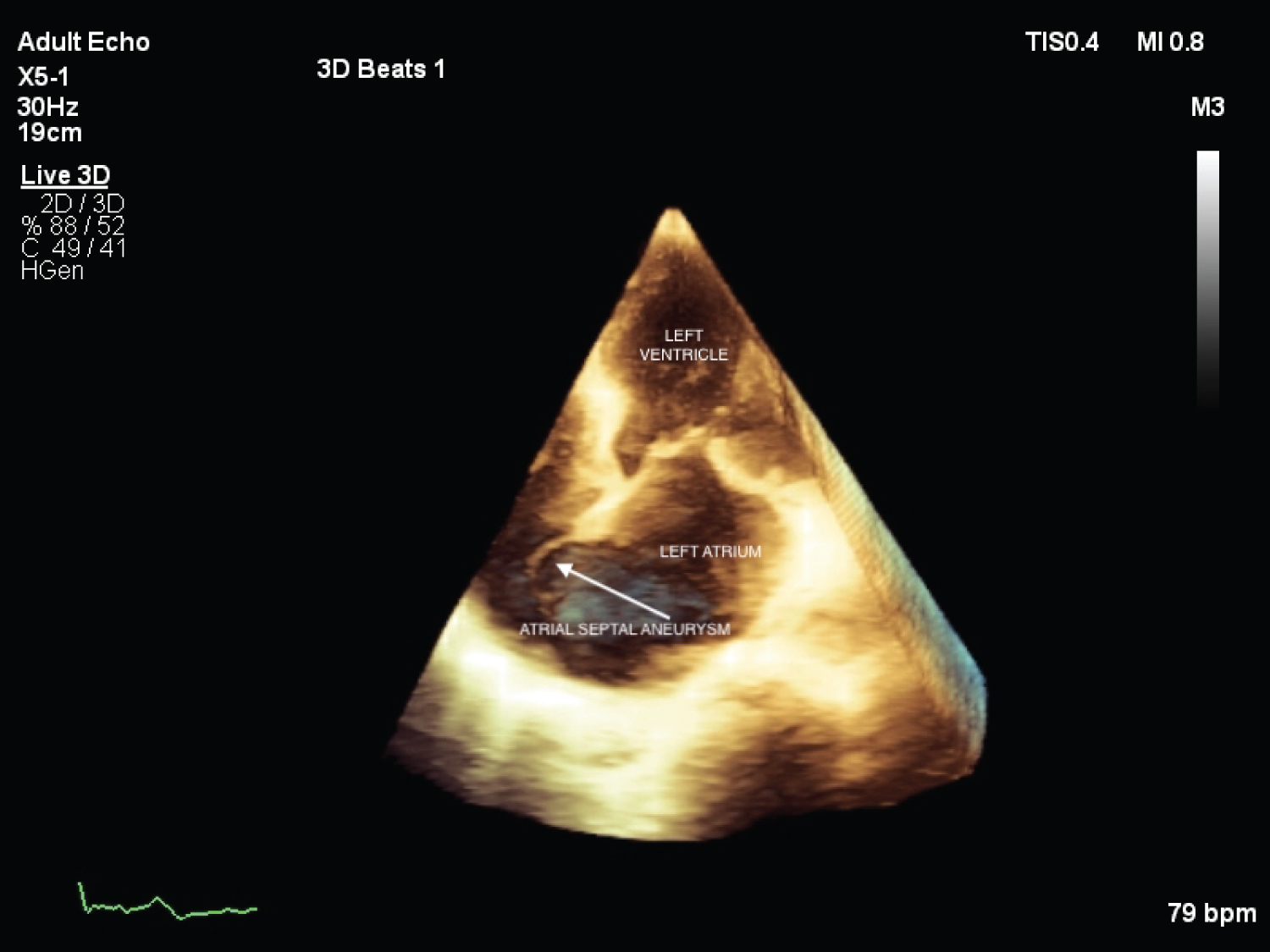
Figure 2: 3D-Echocardiographic image showing atrial septal aneurysm in apical 4 chamber view.
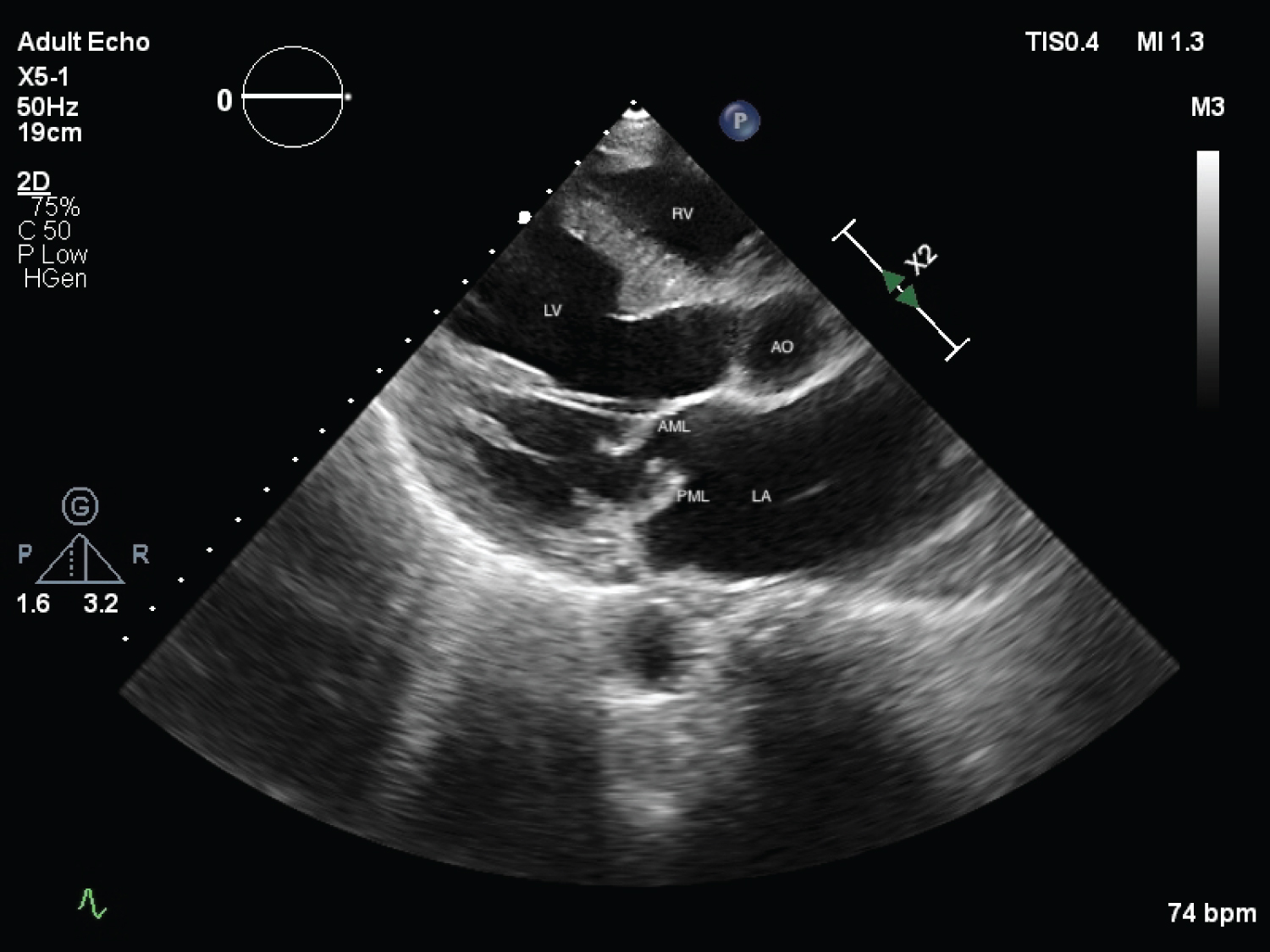
Figure 3: Parasternal Long Axis (PLAX) view on 2D-echocardiography showing prolapse of PML.
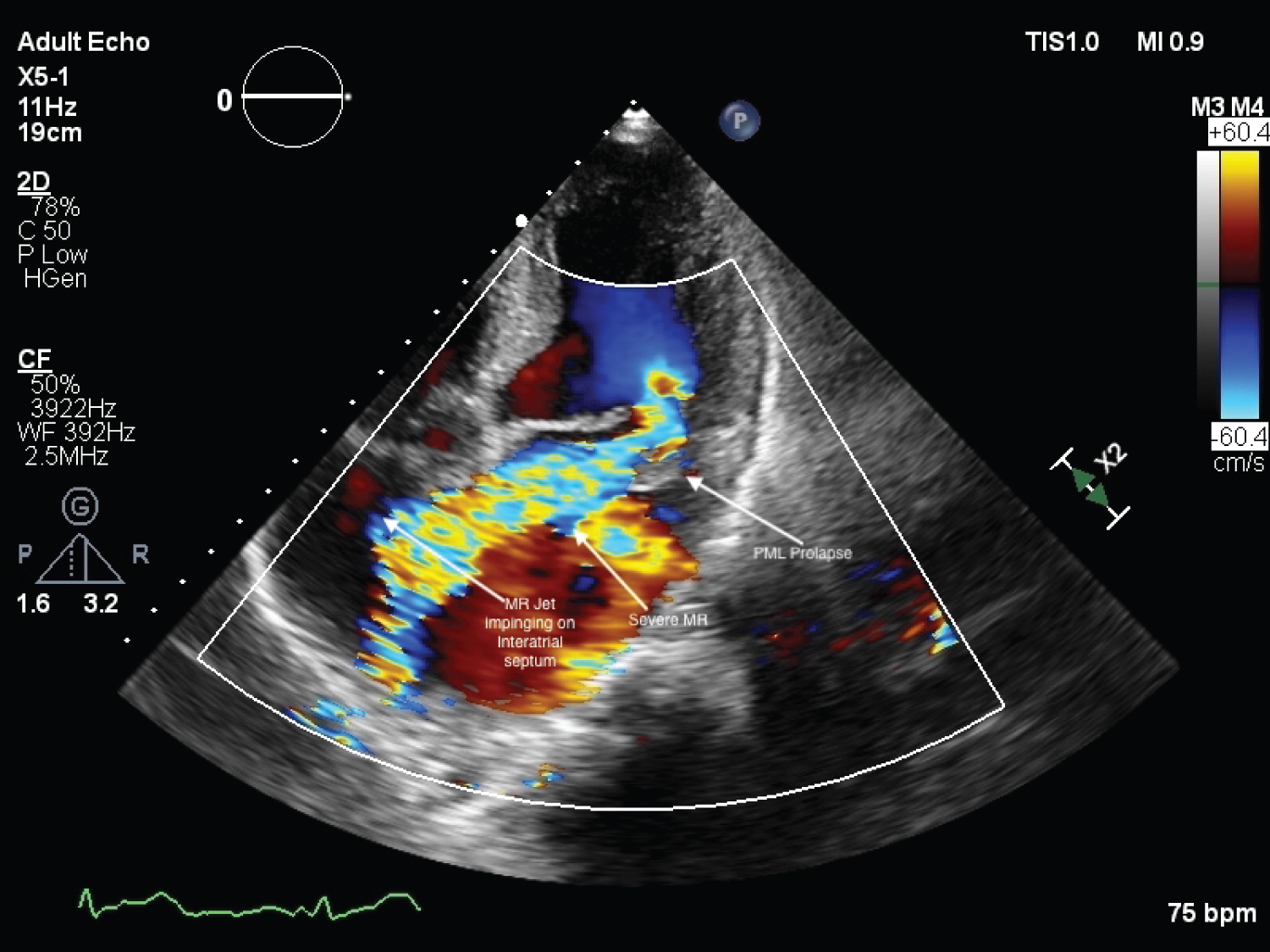
Figure 4: 2D-Echocardiography with color doppler depicting severe eccentric MR jet directed along PML and jet impinging on interatrial septum near atrial septal aneurysm.
Video 1: Apical 4 chamber view showing prolapse of PML, interatrial septal aneurysm & spontaneous echo contrast in left ventricle.
Video 2: 2D-echocardiography PLAX view depicting prolapse of PML.
Video 3: 2D-echocardiography with color doppler showing severe eccentric MR jet impinging on atrial septal aneurysm.