A 13-year-old girl, born from term pregnancy and normal delivery was referred to our institution for signs and symptoms of decompensated heart failure. The patient was polypneic and, jugular engorgement, positive hepatojugular reflux, a 4/6 systolic murmur in the mitral area radiating to the axilla, and a hepatomegaly was observed on physical examination. Chest radiography revealed cardiomegaly. Electrocardiogram revealed sinus rhythm and signs of biatrial overload. Transthoracic echocardiogram revealed a bilobed subvalvular aneurysm, one of the lobes apparently was located in submitral position (Figure 1A) and other in subaortic position (Figure 1B). Severe mitral regurgitation was noted. Systolic pulmonary artery pressure was 58 mmHg. The left ventricular systolic function was maintained. Real-time 3D transthoracic echocardiogram clearly revealed a subaortic aneurysm that was bilobed; the orifice of the aneurysm was unique and was located just below the left coronary cusp (Figure 1C and Figure 1D). These findings were confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging (Figure 1E). The child underwent surgical treatment - closure of the aneurysm neck with a patch, trough the aortic valve, was performed. Plicature of one of the lobes and implantation of a mechanical prosthesis (S Jude 23) in the mitral position was also done. Post-operative period was unremarkable. At discharge transthoracic echocardiography shows a normal function of mechanical valve, and total exclusion of the aneurysm.
Subannular left ventricular aneurysms are classified based on the type of its own orifice - submitral or subaortic. The pathogenesis of these aneurysms is unclear; however, congenital weakness or defects between the ventricular myocardial wall and fibrous valve annulus predisposes one to the development of subannular aneurysms. Subaortic left ventricular aneurysm occurs less frequently compared with a submitral type of subannular aneurysm [1]. Echocardiography is a very effective diagnostic tool for the detection of a congenital subvalvular aneurysm and for the assessment of morphology, location, and possible complications because of the universal availability of the modality and noninvasiveness. However, in last year, others imaging modalities have been used to evaluated this aneurysm [2,3]. This is the first case of subaortic aneurysm studied by three-dimensional echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging, which play a fundamental role in choosing the surgical approach.
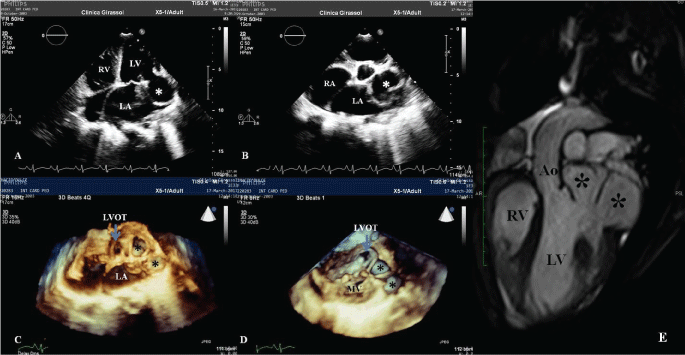
Figure 1: Transthoracic two dimensional echocardiogram revealed a bilobed subvalvular aneurysm, one of the lobes apparently was located in submitral position (A) and other in subaortic position (B). C and D - Real-time 3D transthoracic echocardiogram clearly revealed a subaortic aneurysm that was bilobed. The orifice of the aneurysm was unique and was located just below the left coronary cusp. E - Magnetic resonance imaging that confirm the diagnosis. LA - Left Atrium; LV - Left Ventricle; RV - Right ventricle; LVOT - Left Ventricular Outflow Tract; Ao - Aorta.