International Journal of Neurology and Neurotherapy
Acute Treatment with Renal Denervation in a Patient with Resistant Hypertension and Hemorrhagic Stroke
Francesco Versaci1,2*, Antonio Trivisonno1, Luca Brunese3 and Francesco Prati4
1Department of Cardiovascular Disease, Ospedale "Antonio Cardarelli", Campobasso, Italy
2Department of Cardiovascular Disease, Ospedale "Ferdinando Veneziale", Isernia, Italy
3Department of Medicine and Health Sciences, Università del Molise, Campobasso, Italy
4Department of Cardiovascular Disease, Ospedale "San Giovanni-Addolorata", Rome, Italy
*Corresponding author:
Francesco Versaci, Department of Cardiovascular Disease, Ospedale "Antonio Cardarelli", 86100 Contrada Tappino, Campobasso, Italy, Tel: +390874313427, E-mail: francescoversaci@yahoo.it
Int J Neurol Neurother, IJNN-2-030, (Volume 2, Issue 2), Case Report; ISSN: 2378-3001
Received: July 15, 2015 | Accepted: August 26, 2015 | Published: August 28, 2015
Citation: Versaci F, Trivisonno A, Brunese L, Prati F (2015) Acute Treatment with Renal Denervation in a Patient with Resistant Hypertension and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Int J Neurol Neurother 2:030. 10.23937/2378-3001/2/2/1030
Copyright: © 2015 Versaci F, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Abstract
A 49-year-old man with refractory hypertension was admitted to our hospital in a coma caused by hemorrhagic stroke. Severe hypertension was observed during hospitalization despite a full antihypertensive therapy. Considering the risk of enlargement of the intracranial hematoma, the decision was made to perform renal denervation (RDN). A significant blood pressure reduction was obtained after RDN. The patient had a progressive improvement of general conditions and came out of the coma after a few days. This case underlines the safety and the feasibility of RDN in a critically ill patient.
Keywords
Hypertension, Renal Denervation, Renal Artery Disease Intervention, Resistant hypertension, Hemorrhagic Stroke
Introduction
Renal sympathetic denervation (RDN) is a promising treatment strategy in patients with resistant hypertension [1,2]. It is a catheter-based radio frequency ablation technique to disrupt both afferent and efferent renal nerves, thereby reducing the sympathetic activity between brain and kidney that influences blood pressure [3]. RDN is generally performed as an elective procedure after excluding secondary forms of hypertension. We describe a clinical case of acute treatment with renal denervation in a patient with hemorrhagic stroke due to resistant hypertension.
Case Report
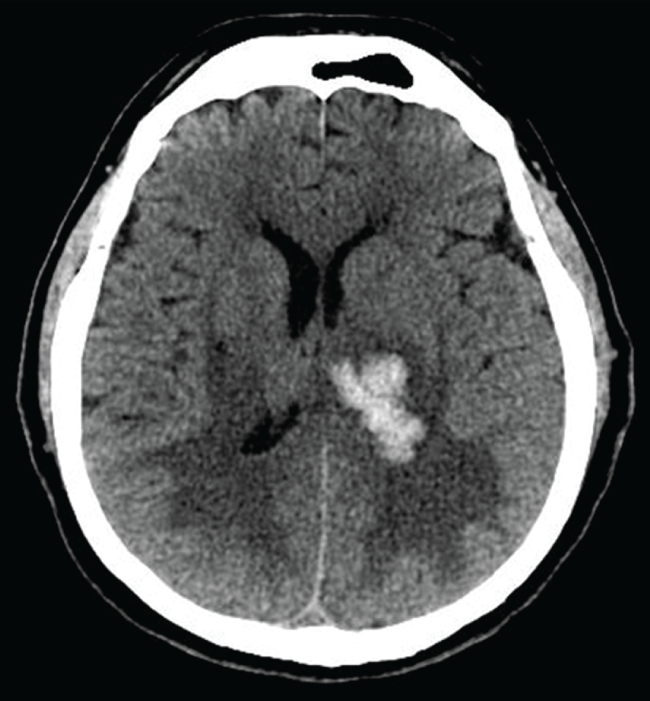
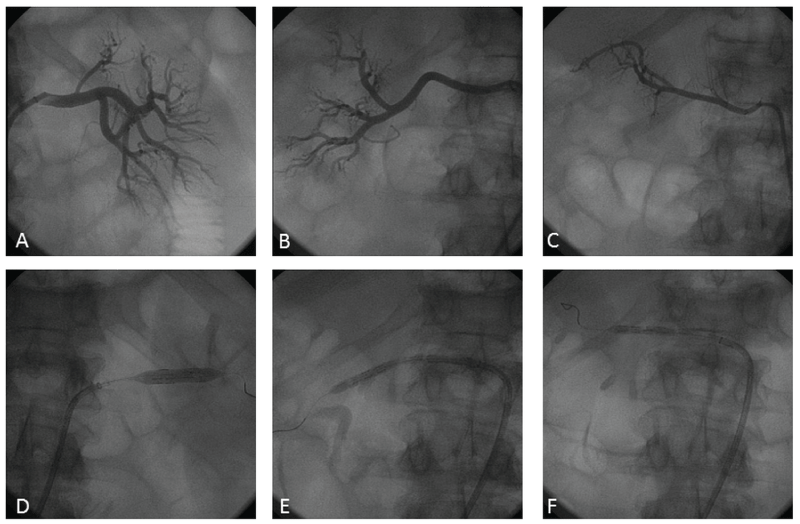
A 49-year-old man with refractory hypertension was admitted to our hospital because of hemorrhagic stroke. Glasgow Coma Scale was 9 and Norton Scale 8. The patient was intubated for controlled mechanical ventilation. Cranial Computed Tomography (CT) scan revealed a left thalamo-capsular hematoma with surrounding edema and mass effect upon the left lateral ventricle (Figure 1). He presented with oliguria (urine output 300 mL daily, creatinine 2.45 mg/dl). ECG showed sinus tachycardia (120 beats/min). The echocardiogram showed normal LV dimensions, concentric hypertrophy and ejection fraction 60%. Renal artery duplex scan revealed no renal artery stenosis. During hospitalization severe hypertension (blood pressure (BP) 210/120 mmHg) was observed despite a full antihypertensive therapy (Bisoprolol 2.5 mg twice daily, Ramipril 10 mg twice daily, Amlodipine 10 mg twice daily, Furosemide 25 mg twice daily, Metolazone 5 mg and urapidil intravenous). After three days, considering the progressive clinical impairment without any possibility of extubation (persistent respiratory acidosis due to pulmonary edema) and high risk of enlargement of the intracranial hematoma, the decision was made to perform RDN. The procedure was planned by using a second generation of radiofrequency device able to delivery energy simultaneously by multiple electrodes (Vessix RDN System, Boston Scientific Corporation). Baseline angiography showed normal lumen of the renal arteries without significant stenosis and a right accessory renal artery. A 4 x 25 mmVessix balloon was used in the right renal artery and in the right accessory renal artery and a 6 x 25 mmVessix balloon was used in the left renal artery without procedural complications (Figure 2). A significant and sustained BP and heart rate (HR) reduction (BP: 130/80 mmHg; HR: 78 beats/min) was obtained immediately after the procedure. In the following days a progressive improvement of general conditions was observed. Renal function recovery was reported with normal diuresis (1500 ml/daily) and creatinine reduction (1.6 mg/dl). The patient came out of the coma and after five days began a neurological rehabilitation program.
.
Figure 1: Cranial computed tomography scan: left thalamo-capsular hematoma (38 cm max) with surrounding edema and mass effect upon the left lateral ventricle.
View Figure 1
.
Figure 2: Baseline (A-B-C) and procedural (D-E-F) angiography of the left (A-D), right (B-E) and right accessory (C-F) renal arteries. Baseline angiography showed normal lumen of the renal arteries without significant stenosis. Procedural angiography showed Vessix RDN balloon inflation into the renal artery causing nerve ablation.
View Figure 2
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first case of acute treatment with RDN in a patient with resistant hypertension and hemorrhagic stroke. We decided to perform RDN in a critically ill patient because a full antihypertensive medical therapy failed to reduce BP values with subsequent clinical impairment and high risk of enlargement of intracranial hematoma. Performing RDN we obtained an immediate, significant and persistent BP reduction, HR normalization and renal function recovery. The BP reduction (systolic BP: -80mmHg and diastolic BP: -40 mmHg) was much larger than that reported in previous trials [1,2] and is in line with the subgroups analysis of Symplicity HTN-3 that underlines the effectiveness of RDN in selected patients with high sympathetic activity such as patients with baseline office BP > 180 mmHg, not-black race patients and young patients [4] or in particular clinical scenarios accompanied by a marked acute sympathetic response as in our case of subarachnoid haemorrhage [5].
In this case no adverse reactions were noted, but a greater amount of studied cases are necessary to confirm the safety of RDN in acute settings. However RDN seems to be a promising strategy for the treatment of malignant hypertension in critically ill patients because it results particularly effective in clinical settings characterized by a high sympathetic activity.
Contributors' Statement
There is no funding source and no conflict of interest.
References
-
Krum H, Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, Böhm M, Mahfoud F, et al. (2014) Percutaneous renal denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: final 3-year report of the Symplicity HTN-1 study. Lancet 383: 622-629.
-
Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, et al. (2010) Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376: 1903-1909.
-
Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Bakris G, Blankestijn PJ, Böhm M, et al. (2013) International Expert Consensus Statement Percutaneous Transluminal Renal Denervation for the Treatment of Resistant Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 62: 2031-2045.
-
Kandzari DE, Bhatt DL, Brar S, Devireddy CM, Esler M, et al. (2015) Predictors of blood pressure response in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Eur Heart J 36: 219-227.
-
Moussouttas M, Lai EW, Huynh TT, James J, Stocks-Dietz C, et al. (2014) Association between acute sympathetic response, early onset vasospasm, and delayed vasospasm following spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci 21: 256-262.